I Sheet You Not¶
Create auto-updating Alfred 3 workflows from Excel worksheets.
Overview¶
I Sheet You Not is a workflow generator/template for Alfred 3. It reads data from an Excel workbook and displays it in Alfred. You can specify which rows and columns the data are read from, and changes to the data are picked up automatically by the workflow.
Download and installation¶
Download the latest version of the workflow from GitHub releases.
Double-click the downloaded I-Sheet-You-Not-X.X.X.alfredworkflow
file to install in Alfred 3.
Usage¶
Tip
Check out the green demo objects in the workflow for examples of how to use and configure I Sheet You Not.
Use the keyword isyn to search for an Excel sheet and generate a new
workflow based on it.
You will be asked to specify a name for your new workflow, which will then be created and added to Alfred.
The red generator elements are removed from auto-generated workflows.
You should then configure the worksheet, first row and data columns in the workflow configuration sheet (if the defaults are unsuitable).
Alter one of the green demo objects in the workflow to suit your purpose (e.g. change the Keyword, Placeholder Title and Subtext) or add your own, then delete the other, unneeded objects.
Configuration¶
Note
What I Sheet You Not calls the VALUE is what is typically referred to
as arg or {query} in Alfred workflow terminology. (arg being
its name in Alfred’s JSON and XML format, and {query} being the text
macro that Alfred replaces with the value of arg). It is the value
passed to subsequent workflow elements when you “action” (i.e. hit ↩ on)
a result shown in Alfred.
By default, the workflow pulls data from the first row of the first worksheet in the workbook. The item title is pulled from column A, the subtitle from column B and the value from column C.
To change these, use the SHEET, START_ROW, TITLE_COL,
SUBTITLE_COL and VALUE_COL options in the workflow configuration
sheet:
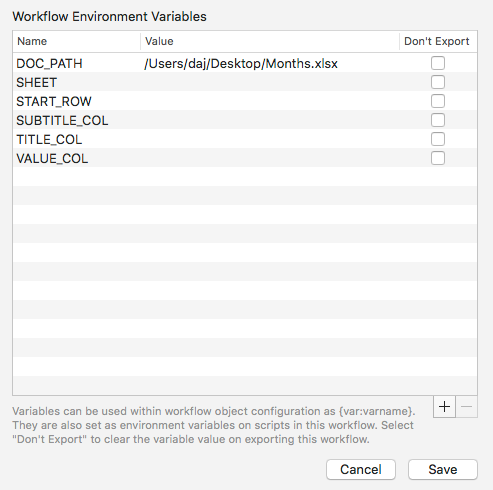
SHEET may be the index number of the worksheet or the title.
If SHEET is unset, it defaults to the first worksheet.
If START_ROW is unset, it defaults to the first row (i.e. 1).
If TITLE_COL is unset, it defaults to the first column (i.e. 1, which
is column A).
If SUBTITLE_COL is unset, it defaults to the column after TITLE_COL.
If VALUE_COL is unset, it defaults to the second column after TITLE_COL.
DATE_FORMAT is a strftime format string that will be used for any
columns that are formatted as dates in the Excel spreadsheet. You can override
this format for specific columns. See Formatting values below.
Important
All rows and columns must be specified as numbers, not letters, so
set TITLE_COL to 1 for column A, 2 for column B etc.
Only the title is required. If there are no data for subtitle or
value in the spreadsheet, set SUBTITLE_COL and/or VALUE_COL to
0.
Command-line options¶
Configuration options may also be specified as options to the isyn
command within the Script Filter:
usage: isyn [-h] [-p FILE] [-m PATTERN] [-n N] [-r N] [-t N] [-s N] [-v N]
[--version]
I Sheet You Not. Search Excel data in Alfred 3. Pass this script the path to
an Excel file via the -p option or the DOC_PATH environment variable. By
default, the script reads the rows of the first worksheet in the workbook and
generates Alfred JSON results. It reads the first three columns, treating the
first as the result title, the second as its subtitle and the third as its
value (arg).
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-p FILE, --docpath FILE
Excel file to read data from. Envvar: DOC_PATH
-m PATTERN, --match PATTERN
sprintf-style pattern for Alfred to match against
(instead of item title). Envvar: MATCH
-n N, --sheet N Number or name of worksheet to read data from. Default
is the first sheet in the workbook. Envvar: SHEET
-r N, --row N Number of first row to read data from. Default is 1,
i.e the first row. Use --row 2 to ignore a title row,
for example. Envvar: START_ROW
-t N, --title N Number of column to read titles from. Default is the
first column. Envvar: TITLE_COL
-s N, --subtitle N Number of column to read subtitles from. Default is
the column after the title column. Set to 0 if there
is no subtitle column. Envvar: SUBTITLE_COL
-v N, --value N Number of column to read values from. Default is the
second column after the title column. Set to 0 if
there is no value column. Envvar: VALUE_COL
--version Show workflow version number and exit.
Extracting data to workflow variables¶
In addition to the title, subtitle and value, you can also extract
additional (or the same) columns to workflow variables, which can be used
by downstream workflow elements. The countries demo included with the
workflow shows this technique.
To create the workflow variable date from column 8 (i.e. H), you would
set the workflow/environment variable VAR_date=8.
For example, the following code would extract data from the first worksheet
in the Excel file, using columns A, B and C (1, 2, 3) as title, subtitle
and value respectively (the default behaviour), and in addition set the
workflow variables url to the data from column D (4) and user to
column E (5):
1 2 3 4 5 6 | # Set workflow variable url from column 4 (D)
export VAR_url=4
# Set workflow variable user from column 5 (E)
export VAR_user=5
./isyn
|
Formatting values¶
I Sheet You Not attempts to format your data according to the type specified
by its formatting in the Excel worksheet. It is able to recognise text, number
and date types. By default, text and number types are formatted “as-is”, while
date types are formatted according to the DATE_FORMAT specified in the
workflow configuration sheet, which is a strftime format string.
(Note that Excel exports currency-formatted columns as plain numbers, so you must specify a format if you’d like to include the currency symbol in ISYN.)
You can specify alternate formats on a per-column basis by setting environment
variables of the form FMT_N, where N is the number of the column:
1 2 3 4 5 | # Format column 3 (C) as YYYY-MM-DD date
export FMT_3='%Y-%m-%d'
# Add currency symbol to column 5 (E)
# Use new-style format string to add commas
export FMT_5='$ {:,.2f}'
|
For text and number types, the formats are interpreted as sprintf-style format strings or Python’s str.format-style format strings. For dates, the formats are interpreted as strftime-style format strings.
Important
When using $ in a format string, you must surround it in
single-quotes (as in the above example), otherwise bash/zsh will
interpret it as a variable, which will fail.
Matching¶
Alfred 3.5 introduced the new match field on items. If specified, Alfred
will filter your results against this field, not the item title.
You can specify the match format using the --match flag to the isyn
command or via the MATCH workflow variable. The match field uses
sprintf-style format strings and named variables. That is to say, you
can only use variables you’ve extracted from your Excel sheet with VAR_xyz
patterns:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | # Extract a couple of variables
export VAR_name=1
export VAR_year=3
# Set the match field to include both
export MATCH='%(name)s %(year)s'
# Use first column (A) for item title and second (B) for subtitle
export TITLE_COL=1
export SUBTITLE_COL=2
|
The above configuration will allow you to filter items by year as well as title.
Feedback, questions, bugs, feature requests¶
If you have feedback or questions regarding I Sheet You Not, please post them in the Alfred forum thread.
If you have a bug report or feature request, please create a new GitHub issue.
Licensing and thanks¶
I Sheet You Not is released under the MIT License. It is based on the xlrd library for Python, released under a BSD-style licence.
The workflow icon was created by carlosjj from IconArchive.com.
Auto-generated API docs¶
This documentation was auto-generated by sphinx from the source code.